 Over 8,000 products in-stock! & FREE 2-Day shipping on all web orders!* Learn More FREE T-Shirt with orders $250+ Details
Over 8,000 products in-stock! & FREE 2-Day shipping on all web orders!* Learn More FREE T-Shirt with orders $250+ Details Notice: Products may be subject to a surcharge added during checkout. Learn More
- Products
- Solutions
- Resources
-
Support
- Technical Support
- Service & Returns
- Trade Shows & Events
- Company Information
- Contacts & Locations
- Contact Us
- Corporate Headquarters
- Worldwide Sales & Service
- Supplier Information
- Supplier Code of Conduct
- Terms & Conditions of Purchase
-
Contact
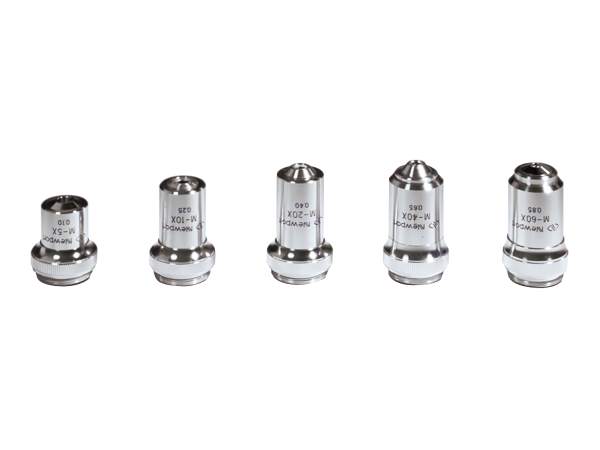
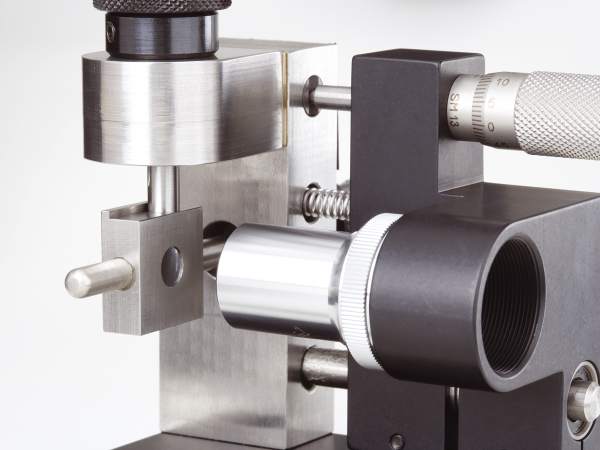













 Ultra-High Velocity
Ultra-High Velocity